




Damage Symptoms : Begins as small, water-soaked spots on leaves, stems, or fruits that enlarge quickly. Fruits develop soft, watery rot with a foul odor, leading to complete collapse. Leaves may wilt and die, causing significant yield loss if untreated.
Survival and Spread : The fungus survives in soil or on plant debris as spores. Spreads via wind, water splash, or contact with infected plants. Spores germinate in humid conditions, infecting through wounds or natural openings.
Favourable Conditions : High humidity (above 90%), temperatures 25-30°C, and poor air circulation. Common in tropical or subtropical climates during rainy seasons, exacerbated by overcrowding or overhead irrigation.
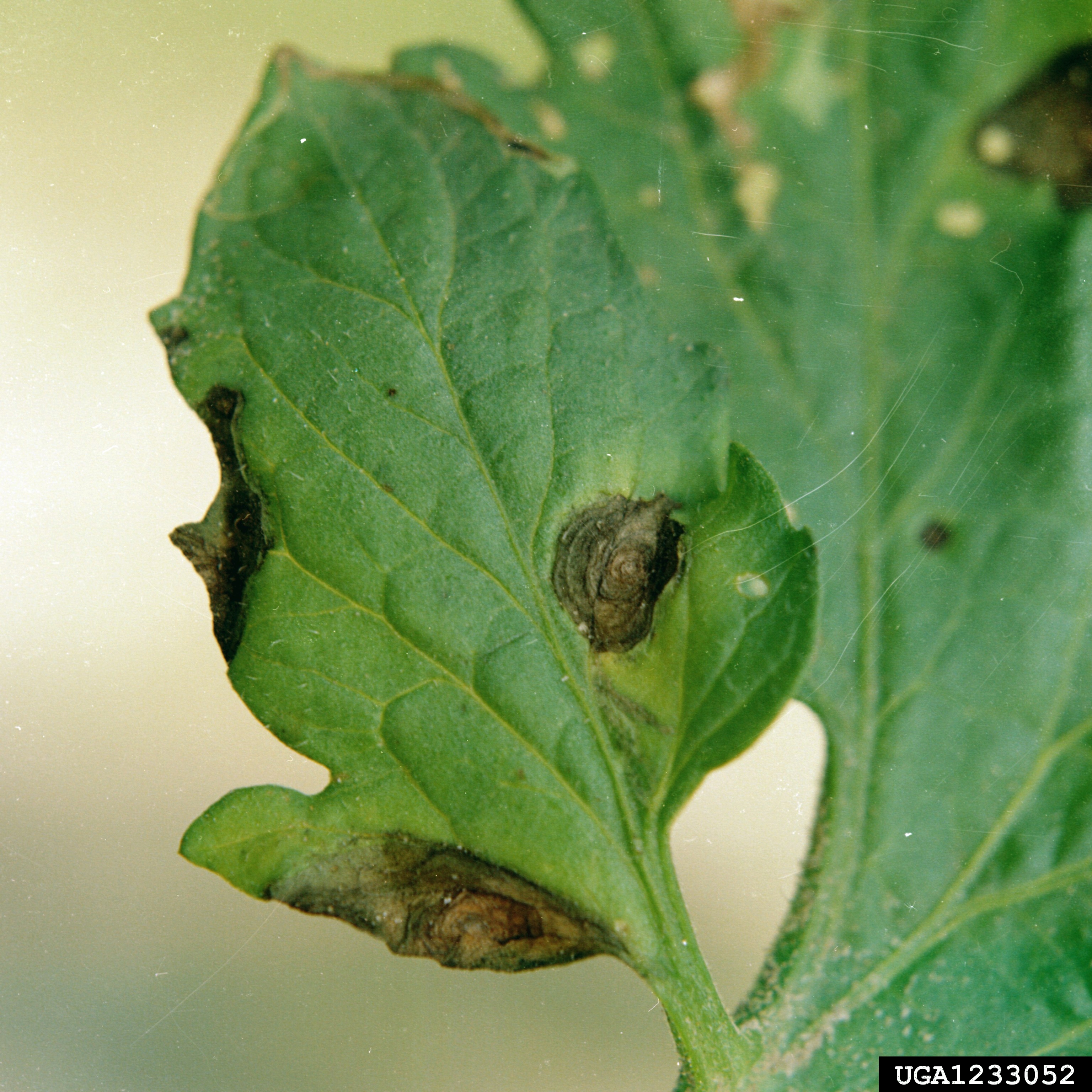
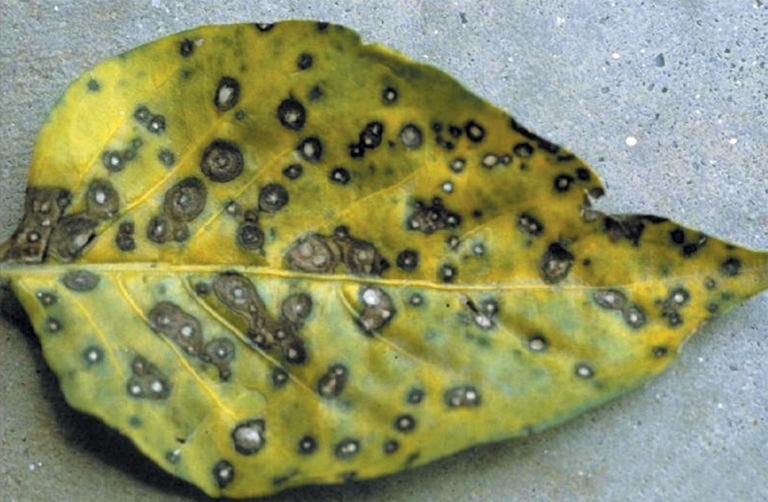





Damage Symptoms : Circular to irregular spots on leaves, starting small and expanding to 1-2 cm, with concentric rings. Severe infections lead to leaf yellowing, curling, and premature drop. Fruits may show sunken lesions, reducing quality and yield.
Survival and Spread : Fungal spores survive on infected plant debris or seeds. Spreads through wind, rain, or splashing water. Can overwinter in soil and infect via spores landing on susceptible tissue.
Favourable Conditions : Warm, humid weather (20-30°C/68-86°F) with frequent rain or dew. High relative humidity (80-90%) and wet foliage promote spore germination. Common in late season or in fields with poor drainage.
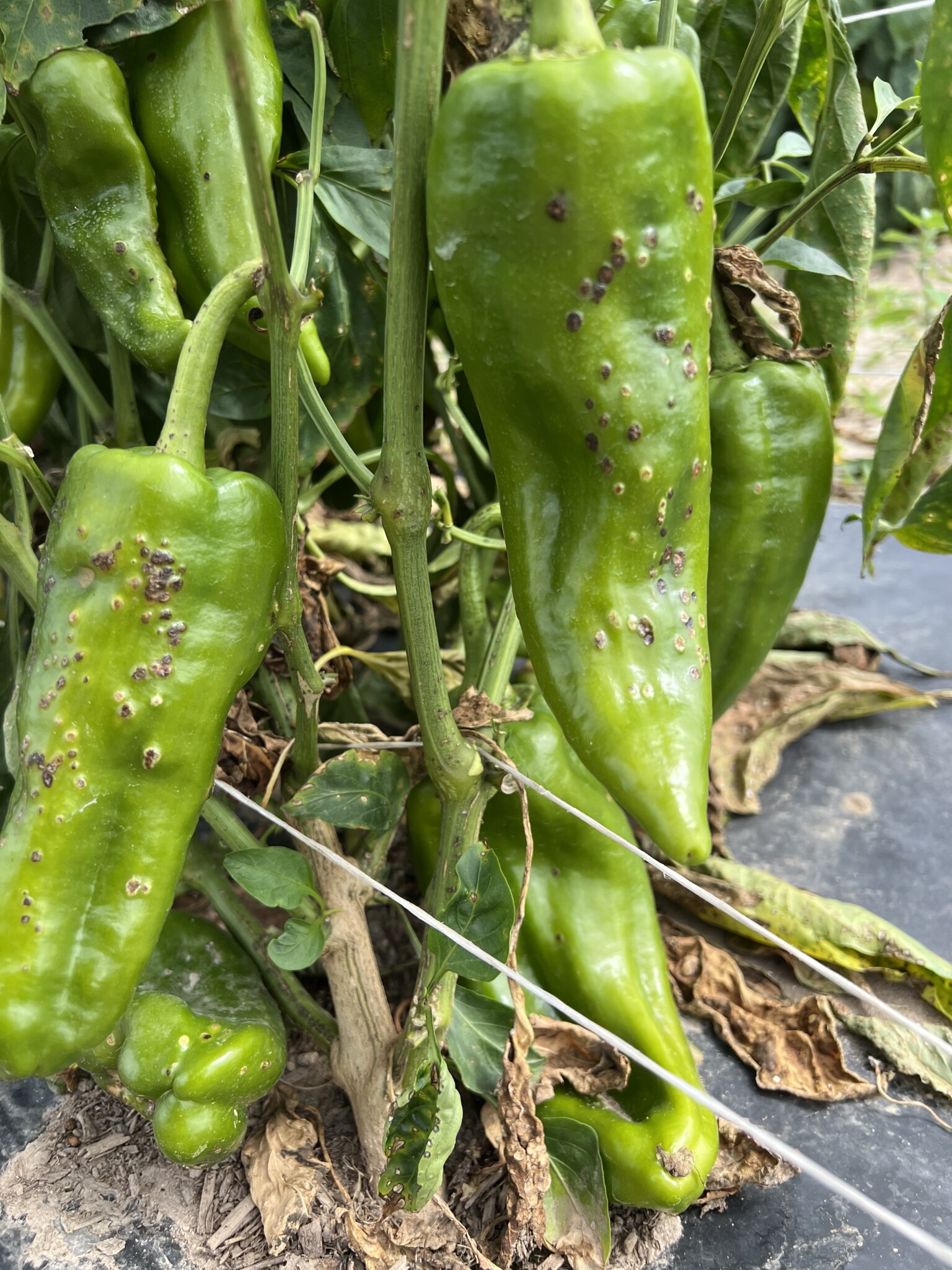
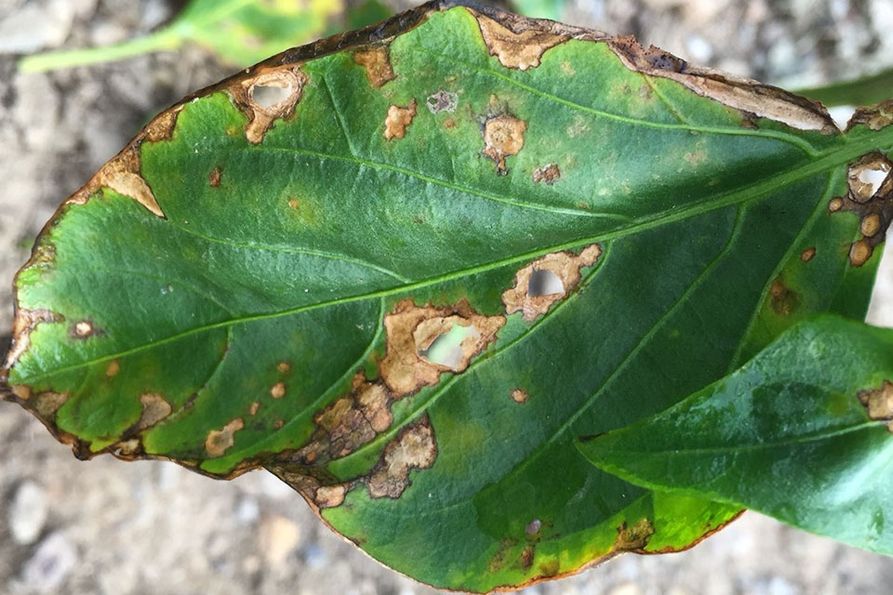
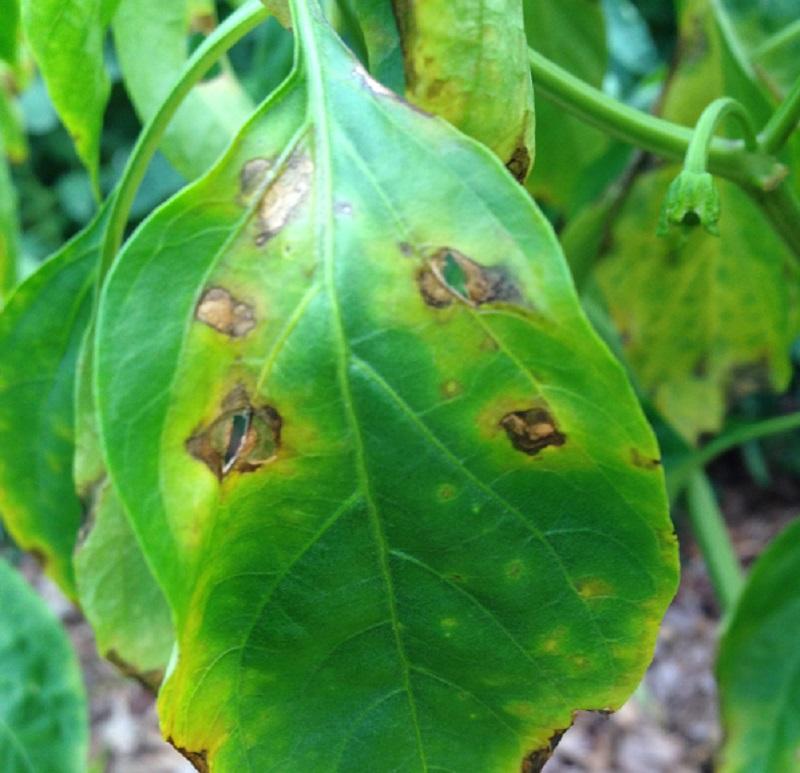





Damage Symptoms : Starts as tiny, dark lesions on leaves that enlarge and become necrotic. Leaves develop chlorosis around spots, leading to defoliation. Fruits may have raised, scabby lesions, causing cracking and reduced marketability.
Survival and Spread : Bacteria survive in seeds, plant debris, or weeds. Spreads via water splash, wind-driven rain, or contaminated tools/equipment. Can enter through stomata or wounds.
Favourable Conditions : Warm, wet environments (25-30°C/77-86°F) with high humidity and frequent rainfall. Overhead irrigation or heavy dew favors spread, overcrowding increases disease pressure.
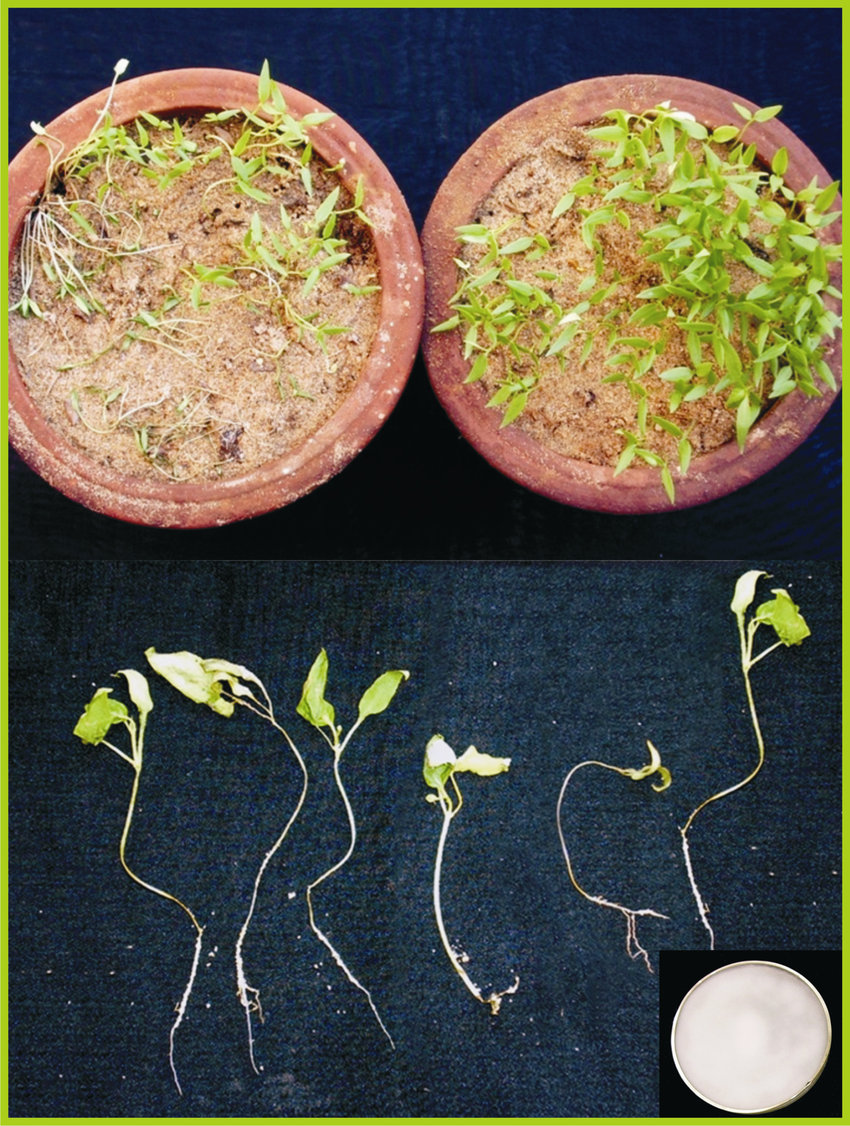

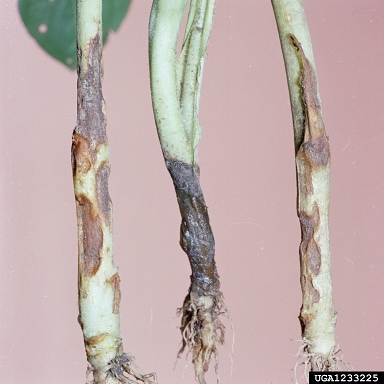


Damage Symptoms : Primarily affects seedlings: stems constrict and rot at the base, causing wilting and death. Roots become soft and discolored. In older plants, it can cause root rot, stunting growth and reducing vigor.
Survival and Spread : Pathogens persist in soil as spores, mycelium, or sclerotia. Spreads through contaminated soil, water, or infected transplants. Often introduced via poor-quality seeds or infested potting mix.
Favourable Conditions : Cool, wet soil (10-20°C/50-68°F) with high moisture and poor drainage. Overwatering, overcrowding, and low light exacerbate it. Common in nurseries or early growth stages.
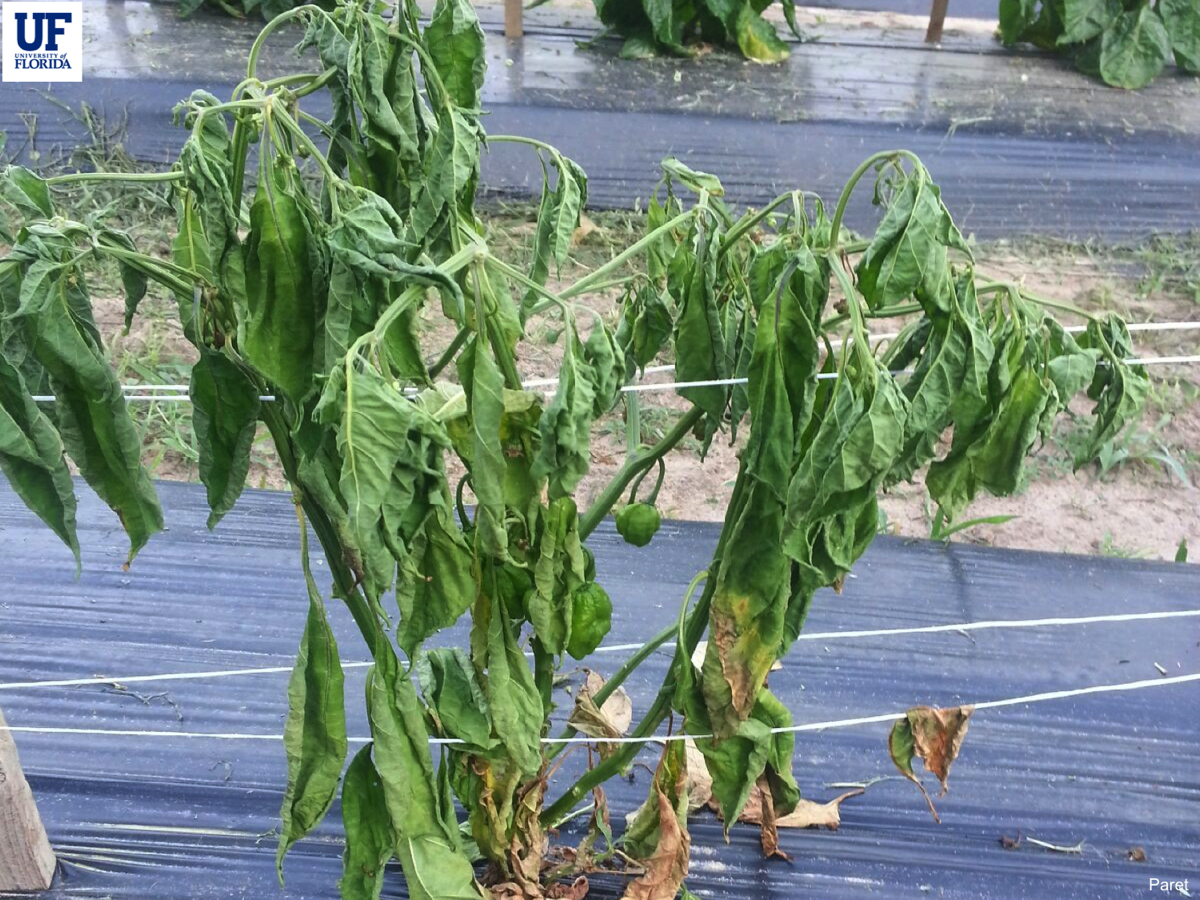






Damage Symptoms : Leaves yellow and wilt, starting from the bottom and progressing upward. Stems exhibit brown discoloration in vascular tissues. Fruits may be small and distorted; severe cases lead to plant death.
Survival and Spread : Fungus survives in soil as chlamydospores for years. Spreads via infected soil, water, or transplants. Not seed-borne but can contaminate roots.
Favourable Conditions : Soil temperatures 25-30°C (77-86°F), moderate moisture, and acidic to neutral pH. Stress factors like nutrient deficiencies or root damage increase susceptibility. Prevalent in warm climates with continuous cropping.
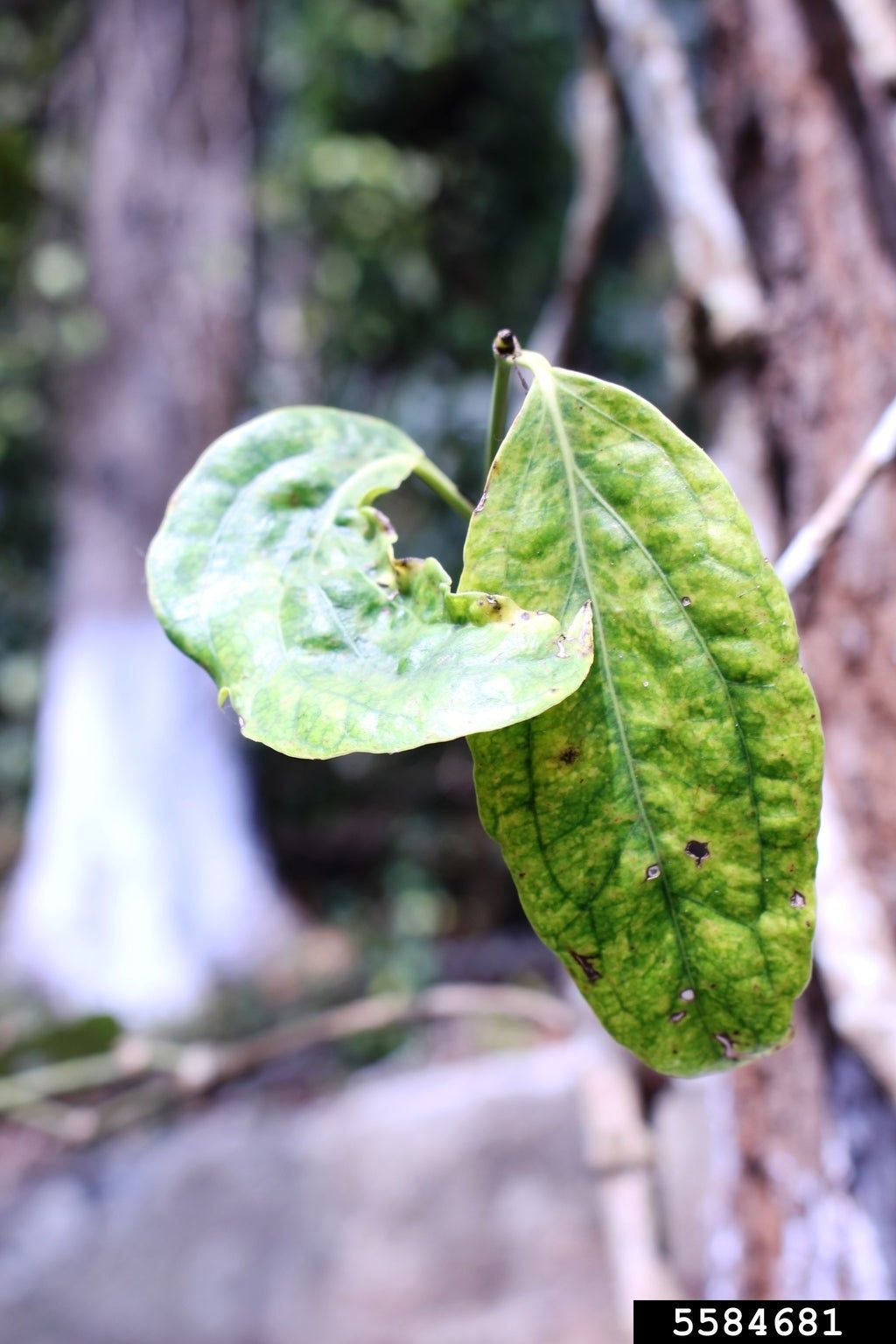




Damage Symptoms : Leaves show chlorotic mottling, curling, and vein clearing. Plants stunt, with fewer and deformed fruits. Symptoms vary by virus but often include yellowing and reduced vigor.
Survival and Spread : Viruses persist in infected plants or seeds. Spread by aphids, thrips, or mechanical means (e.g., contaminated tools). Can overwinter in weeds or perennial hosts.
Favourable Conditions : Mild temperatures (15-25°C/59-77°F) with high insect vector activity. Stress from drought, nutrient imbalance, or extreme weather promotes symptom expression. Common in areas with aphid populations.
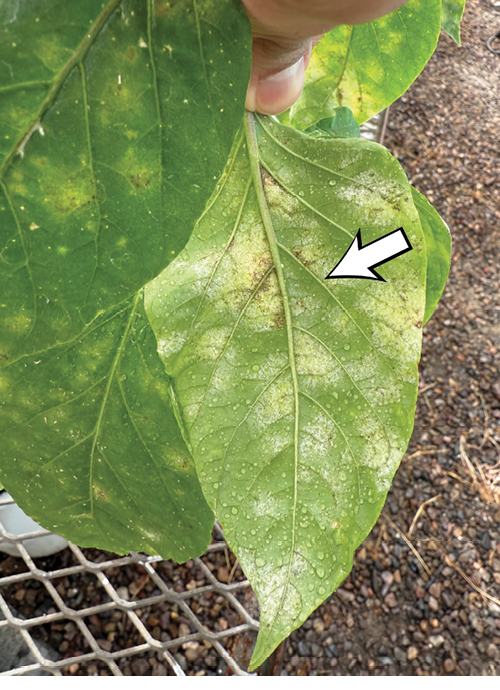
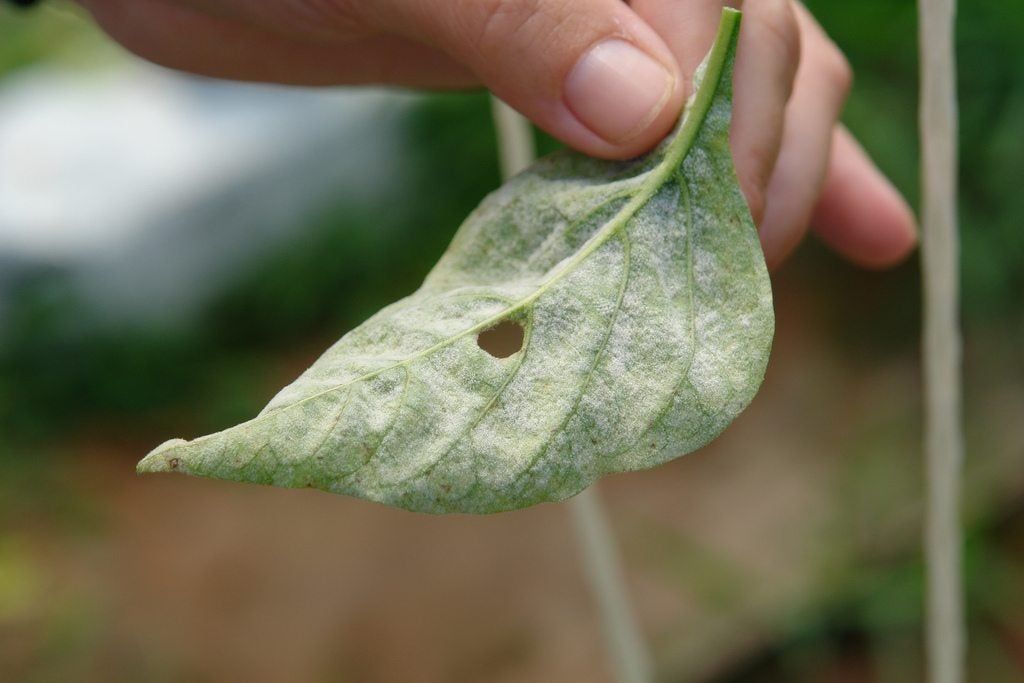
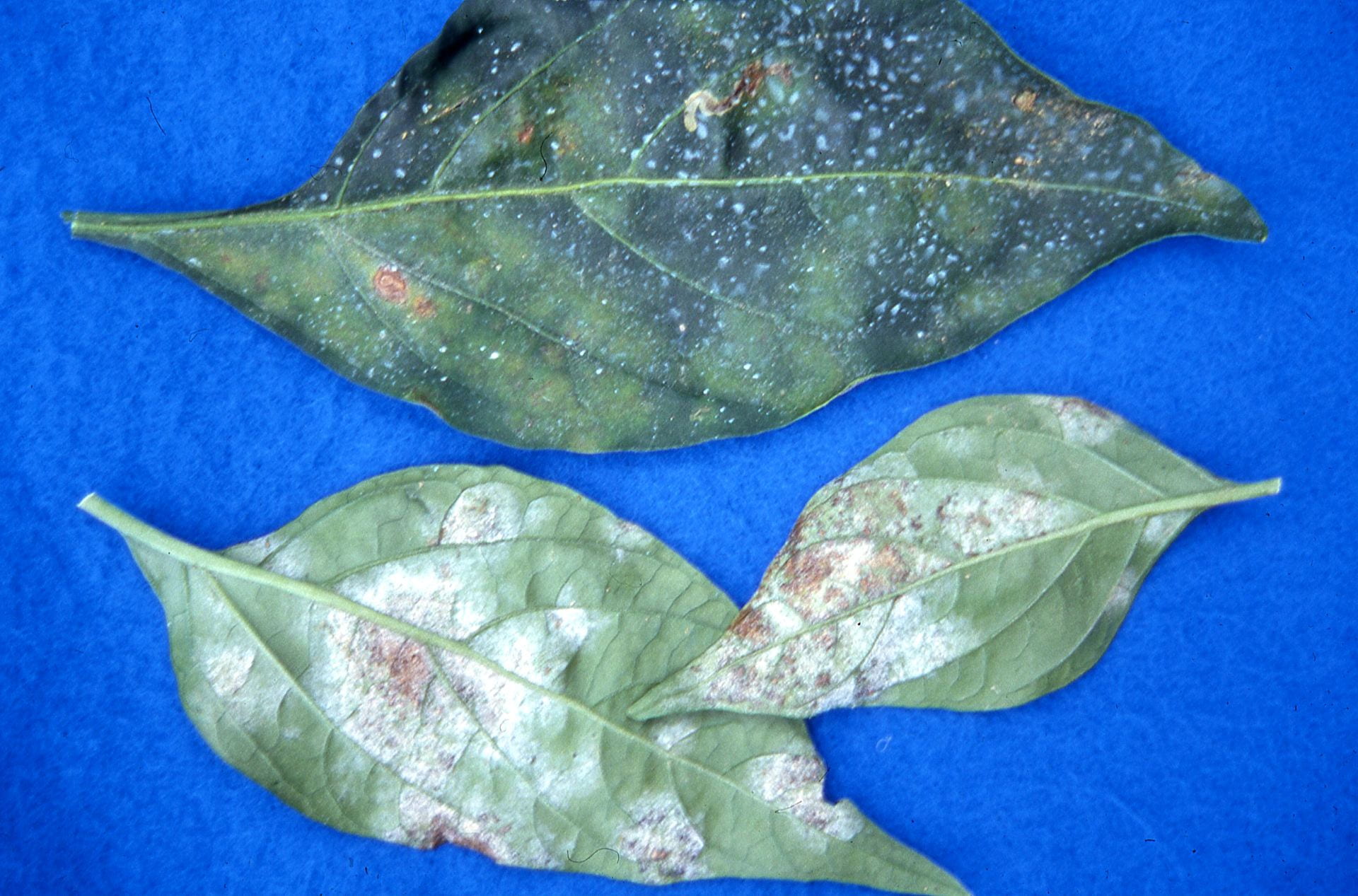





Damage Symptoms : White, powdery patches on leaves, stems, and fruits, leading to chlorosis and necrosis. Leaves curl and drop prematurely, reducing photosynthesis and yield. Fruits may develop russeting.
Survival and Spread : Fungus overwinters as mycelium or spores on plant debris. Spreads via wind-borne spores. Can infect through stomata without wounds.
Favourable Conditions : Moderate temperatures (20-25°C/68-77°F) with low humidity but high relative humidity at night. Shaded, dense plantings and poor air circulation favor it. Common in greenhouses or humid regions.